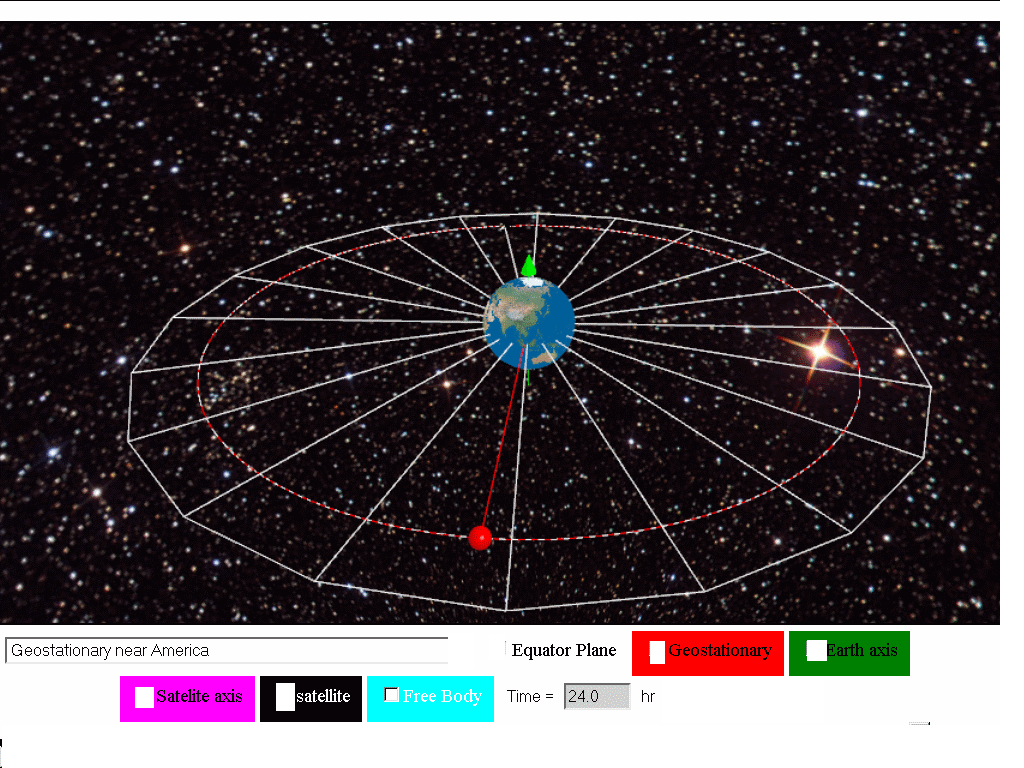
Image satellites in geostationary orbit by lookang many thanks to author of original simulation francisco esquembre author of easy java simulation francisco esquembre.
Calculate the orbital height of a geostationary satellite.
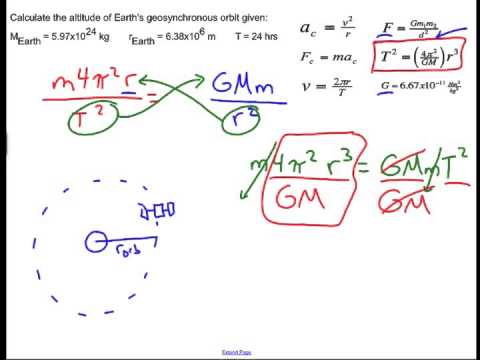
Through the use of re arranging the above equation we can come to the equation.
R g m2 t 4π we know that m2 is the mass of the earth at 5 98 10 24 kg t is the time period and g the universal gravitation constant at 6 67 x10 11 kg 2.
From earth they would seem drifting in westerly direction.
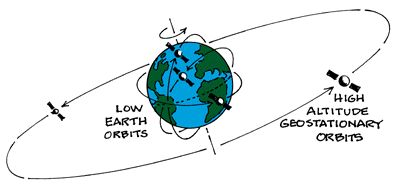
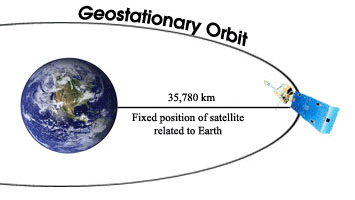
A geostationary orbit also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit geo is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35 786 kilometres 22 236 miles above earth s equator and following the direction of earth s rotation.
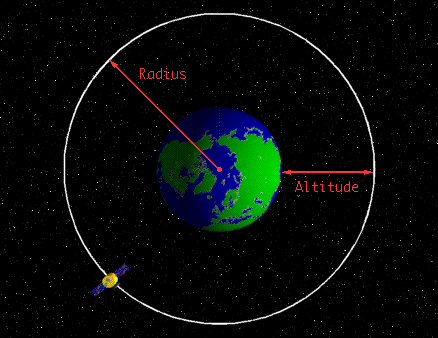
H is the altitude height of the object.
The satellite must have a period.
Speed of a satellite in circular orbit orbital velocity period centripetal force physics problem duration.
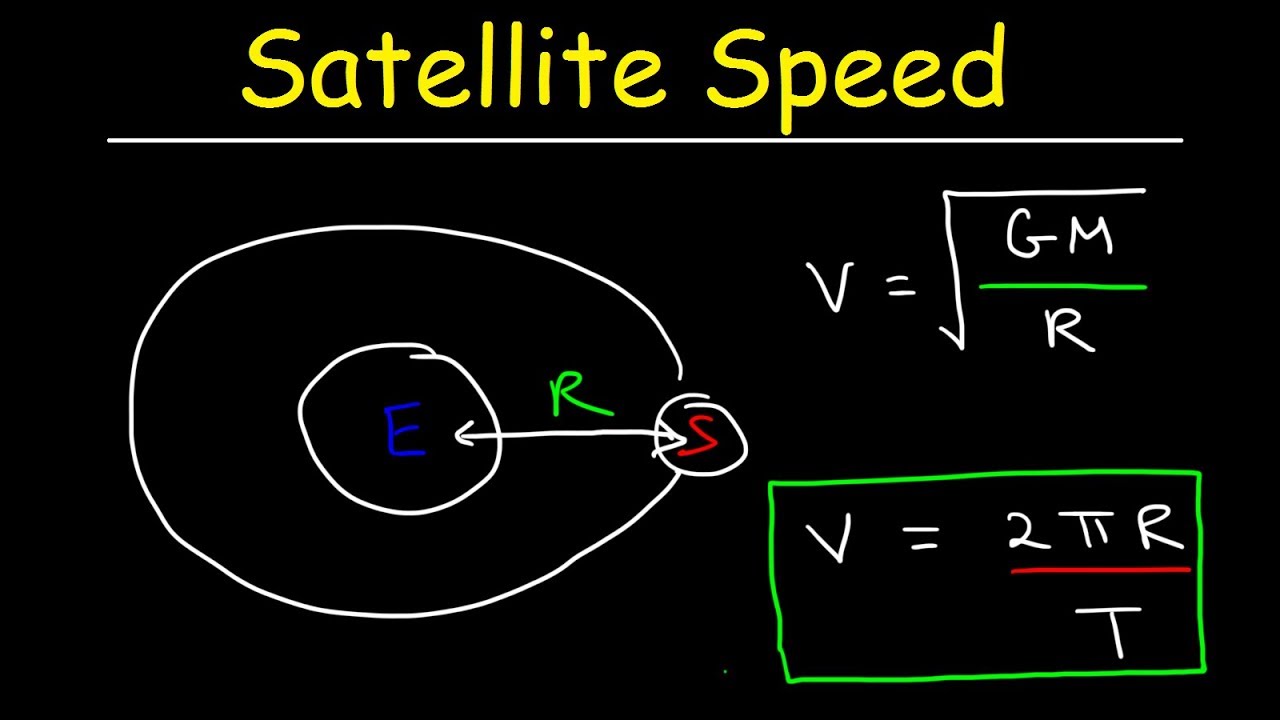
P is the orbital period.
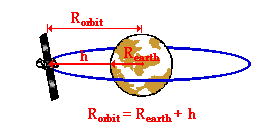
R orbital radius earth s equatorial radius height of the satellite above the earth surface r 6 378 km 35 780 km r 42 158 km r 4 2158 x 107 m speed.
H 4 22 10 7 6 37 10 6 3 583 10 7 m.
An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to the earth s rotational period one sidereal day and so to ground observers it appears motionless in a fixed.
We can calculate the height h above the earth s surface by subtracting the radius of the earth from the radius of the orbit.
The organic chemistry tutor 143 911 views 17 18.
The height of the geostationary orbit is 35786 kilometers above earth in geostationary orbit the satellite moves with an orbital speed of 11068 km per hours.
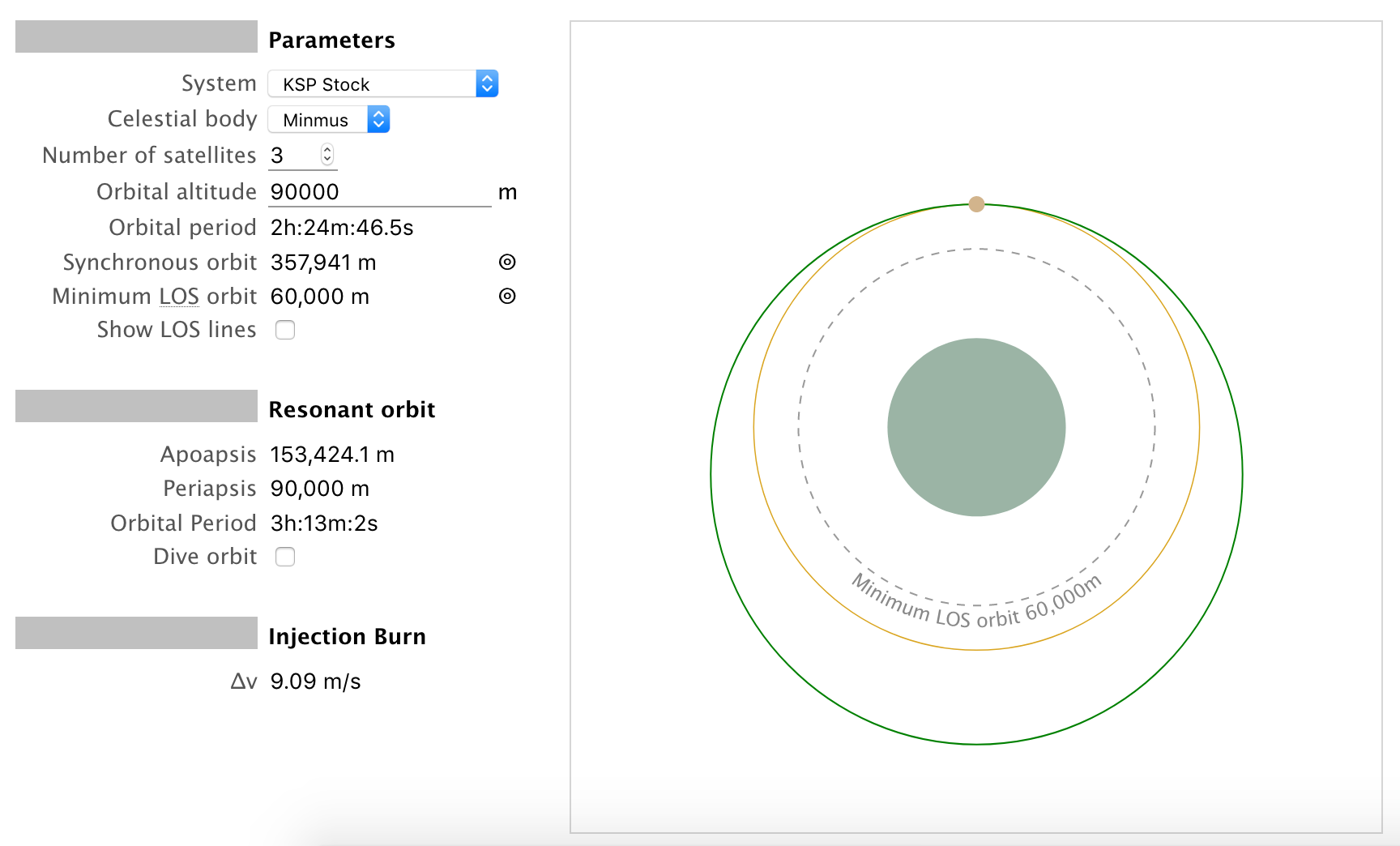
A minimum of three satellites are needed to cover the entire earth super synchronous orbit is a disposal storage orbit above gso.
Because the radius and period are related you can use physics to calculate one if you know the other.
B calculate the height at which the satellite orbits above the surface of the earth.
To calculate the radius of a geostationary orbit the centripetal force must equal the gravitational force on the satellite or mass.
An object s orbital altitude can be computed from its orbital period and the mass of the body it orbits using the following formula.
G is the gravitational constant.
Mission control wishes to place a satellite in circular orbit above the earth.
When a satellite travels in a geosynchronous orbit around the earth it needs to travel at a certain orbiting radius and period to maintain this orbit.
The period of a satellite is the time it takes.